
DNA polymerases have proofreading activity, and a DNA repair enzymes have evolved to correct these mistakes.
This leads to mismatched base pairs, or mispairs. Errors occur in DNA replication, when the incorrect base is incorporated into the growing DNA strand. The initiation of DNA replication at the leading strand is more complex and is discussed in detail in more specialized texts.ĭNA polymerases in DNA replication Simplified representation of the action of DNA polymerases in DNA replication in bacteria Mistakes in DNA replicationĭNA replication is not perfect. The gap is filled by DNA ligase, an enzyme that makes a covalent bond between a 5'-phosphate and a 3'-hydroxyl group ( Figure 3). This leaves a gap between the 3'-end of the newly synthesized DNA and the 5'-end of the DNA previously synthesized by Pol III. At this point Pol I takes over, using its 5'- to 3'-exonuclease activity to digest the RNA and fill the gap with DNA until it reaches a continuous stretch of DNA. Pol III can then take over, but it eventually encounters one of the previously synthesized short RNA fragments in its path. This is produced in the lagging strand by an RNA polymerase (called DNA primase) that is able to use the DNA template and synthesize a short piece of RNA around 20 bases in length.
#TRANSCRIPTIONS AND TRANSLATION OF DNA FREE#
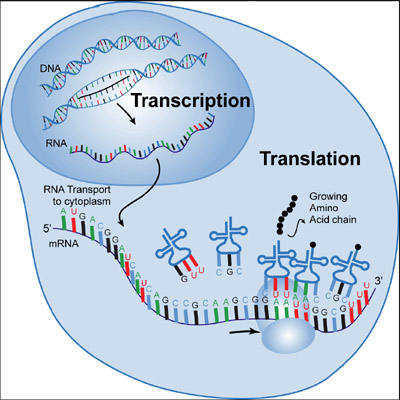
Strangely, DNA polymerases cannot initiate DNA synthesis de novo, but require a short primer with a free 3'-hydroxyl group. Bacteria have at least three distinct DNA polymerases: Pol I, Pol II and Pol III it is Pol III that is largely involved in chain elongation. The resulting short strands are called Okazaki fragments (after their discoverers, Reiji and Tsuneko Okazaki). The leading strand is synthesized continuously but the opposite strand is copied in short bursts of about 1000 bases, as the lagging strand template becomes available. A portion of the double helix must first unwind, and this is mediated by helicase enzymes. This makes it impossible for DNA polymerases to synthesize both strands simultaneously. The Central Dogma of Molecular Biology states that DNA makes RNA makes proteins ( Figure 1).ĭNA replication in bacteria Simplified representation of DNA replication in bacteriaĭNA biosynthesis proceeds in the 5'- to 3'-direction. This is a fascinating subject that is certain to advance rapidly over the next few years. Some of this non-coding DNA controls gene expression but the purpose of much of it is not yet understood.

The nucleotide sequence of the human genome is now known to a reasonable degree of accuracy but we do not yet understand why so much of it is non-coding. These regions are called introns and make up around 95% of the genome.
#TRANSCRIPTIONS AND TRANSLATION OF DNA CODE#
Large stretches of DNA in the human genome are transcribed but do not code for proteins. The human genome contains around 30 000 genes, each of which codes for one protein. This is known collectively as the human genome. In humans, the nucleus of each cell contains 3 × 10 9 base pairs of DNA distributed over 23 pairs of chromosomes, and each cell has two copies of the genetic material. The genetic material is stored in the form of DNA in most organisms.


 0 kommentar(er)
0 kommentar(er)
